How to calculate the ideal battery size and number of batteries for your needs with our Battery Backup Calculator. Understand battery types, functionalities, and make informed decisions for your energy solutions
Battery Backup Calculator
energy-dependent world, having a reliable battery backup system is essential for ensuring your devices remain powered during outages or when access to electricity is limited. Our Battery Backup Calculator helps you determine the right battery size and number of batteries based on your energy consumption needs. Whether you’re looking to power your home, business, or specific appliances, this tool will provide you with accurate estimates to optimize your battery usage.
Understanding Battery Size and Number of Batteries
To effectively calculate your battery requirements, it’s crucial to understand a few key concepts:
- Battery Size: This refers to the capacity of the battery, typically measured in Ampere-hours (Ah). It represents the amount of energy the battery can store and supply over a certain period.
- Number of Batteries: Depending on your energy needs, you might require more than one battery. This is especially true if you are powering multiple devices or appliances.
- Load and Consumption: Load refers to the total power (in Watts) required by the devices you plan to run. Understanding your consumption patterns helps in determining the right battery configuration.
- Formula for Calculation: The formula to estimate the backup time is:
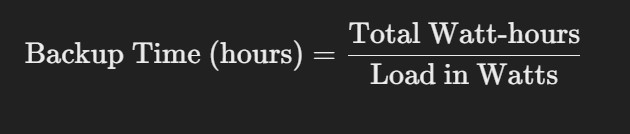
- Total Watt-hours = Number of Batteries × Battery Capacity (Ah) × Battery Voltage (V) × Efficiency (%)
Types of Batteries
When it comes to battery backup systems, several types of batteries are commonly used. Each type has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages:
- Lead Acid Batteries:
- Functionality: The most traditional and widely used type, lead-acid batteries are reliable and cost-effective. They come in two varieties: flooded and sealed (AGM/gel).
- Best for: Applications where weight is not a significant concern, such as stationary power backup systems.
- Lithium-ion Batteries:
- Functionality: These batteries are lighter and more efficient than lead-acid batteries. They have a longer lifespan and can be discharged deeper without damaging the battery.
- Best for: Portable applications, electric vehicles, and situations where space and weight are critical.
- Nickel-Cadmium Batteries:
- Functionality: Known for their robustness and ability to operate in extreme temperatures, nickel-cadmium batteries are less common but still used in specific applications.
- Best for: Applications requiring long service life and reliability.
Materials and Functionality
The materials used in battery construction can significantly affect performance. For instance:
- Lead-acid batteries use lead dioxide and sponge lead, offering a high surge current, making them suitable for starting engines.
- Lithium-ion batteries utilize lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate, providing high energy density and efficiency, ideal for modern applications like smartphones and electric vehicles.
Strength and Durability
Battery strength refers to the ability to deliver power efficiently over time. Factors influencing this include:
- Cycle Life: The number of charge/discharge cycles a battery can handle before its capacity significantly diminishes. Lithium-ion batteries typically offer a higher cycle life compared to lead-acid batteries.
- Temperature Tolerance: Some batteries perform better in extreme temperatures, which is vital for outdoor or unconditioned storage environments.
Which is Better: Lithium or Lead Acid?
When deciding between lithium and lead-acid batteries, consider:
- Cost vs. Performance: While lithium batteries have a higher upfront cost, their longevity and efficiency can lead to lower total ownership costs.
- Weight: Lithium batteries are significantly lighter, making them ideal for portable applications.
- Depth of Discharge: Lithium batteries can typically be discharged to a greater extent than lead-acid batteries without harming their lifespan.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of battery backup systems is essential for making informed decisions about your energy needs. By utilizing our Battery Backup Calculator, you can determine the ideal battery size and configuration, ensuring that you remain powered when it matters most. Explore the various battery types, their materials, and functionalities to choose the best option for your specific requirements.
FAQs
Q: How do I calculate the number of batteries I need?
A: Use the formula mentioned earlier to determine the total watt-hours required, and divide that by the watt-hours provided by each battery.
Q: Can I use different types of batteries together?
A: It’s generally not recommended to mix different types of batteries, as they can have different charging and discharging characteristics.
Q: What is the lifespan of a typical battery?
A: Lead-acid batteries usually last 3-5 years, while lithium-ion batteries can last 10 years or more with proper care.
Q: How do I maintain my batteries?
A: Regularly check the battery’s state of charge, clean terminals, and ensure proper ventilation to extend their life.